
Introduction
Sustainable procurement means looking beyond price and quality to include environmental and social factors when buying goods and services. It’s a strategic approach that aligns a company’s supply chain with wider goals like environmental protection and social responsibility. In practice, embracing sustainable procurement can build brand value, satisfy eco-conscious customers, drive innovation, and strengthen resilience across the business. Below, we break down the main drivers into four categories – Market Advantages, Operational Resilience, Social Responsibility, and Organizational Culture – to show why organizations are investing in sustainable purchasing.
Market Advantages
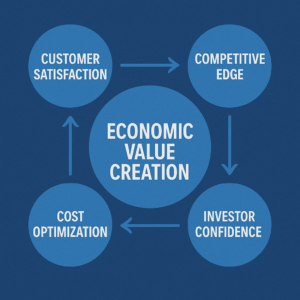
Sustainable procurement delivers clear market and financial benefits. For example, many customers now expect products that are safe, eco-friendly, and accessible. Meeting these expectations can boost loyalty and satisfaction. Research shows that a sustainable strategy enhances reputation and brand image, which in turn helps sustain brand loyalty and attract new customers. In competitive markets, companies with a strong green or ethical value proposition stand out and may gain an edge over peers. Sustainable practices also appeal to investors: improving environmental/social governance (ESG) ratings makes a company more attractive to shareholders and can strengthen its reputation among conscious consumers and investors.
Customer Satisfaction: Buying from suppliers that offer safety, environmental benefits, and inclusive design helps meet today’s consumer demands. This focus on sustainability reinforces customer loyalty and can expand the customer base.
Competitive Edge: Firms that source sustainably can differentiate their products or services. A clear sustainability angle – from recycled materials to fair labor – builds brand reputation and signals innovation, helping a company stand out in crowded markets.
Investor Confidence: Companies known for sustainable procurement often score higher in ESG ratings. That attracts investors and improves access to capital, since financial backers increasingly favor organizations with strong environmental and social performance.
Cost Optimization: Sustainable procurement often means using resources more efficiently and reducing waste. Studies find it can cut procurement costs by roughly 9–16% through measures like reducing over-specification, lowering consumption, and boosting energy efficiency. Over time, these savings add up, freeing funds for reinvestment.
Economic Value Creation: By analyzing total life-cycle costs and benefits, organizations make smarter choices that create long-term value. In fact, effective sustainable procurement has been linked to raising revenue by 5–20% (through new sales and markets) while cutting costs. Together, these outcomes show sustainability can drive profitability as well as purpose.
Operational Resilience
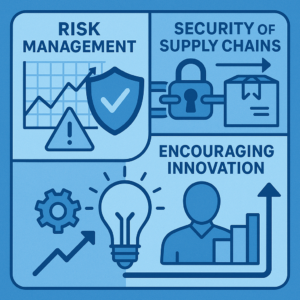
Sustainability in procurement also strengthens the day-to-day operations and supply chains. By selecting suppliers who meet environmental and social standards, businesses can reduce exposure to risks that could disrupt operations. For instance, working with responsible vendors helps avoid legal issues, scandals, or recalls that harm a brand. In an interconnected world, a company’s reputation is a key asset, and sustainable procurement helps safeguard it by reducing supply chain risks and ensuring compliance with evolving regulations. In essence, considering sustainability is a risk-management strategy.
Risk Management: Ignoring sustainability risks (like pollution, labor abuses or regulatory breaches) can damage brand value and lead to costly liabilities. Sustainable procurement helps mitigate these risks. It ensures suppliers comply with environmental and social regulations, which protects the company from fines and negative publicity.
Security of Supply Chains: Prioritizing sustainability makes supply chains more reliable. If a company works with well-audited, responsible suppliers, it is less likely to face sudden disruptions (such as supplier failures or resource shortages). Continuous improvement – like finding alternatives before resources deplete – ensures goods keep flowing even under stress. This “future-proofing” of supply chains is a core benefit of sustainable sourcing.
Encouraging Innovation: Engaging suppliers on sustainability topics often sparks new ideas. When companies treat carbon emissions or waste as problems to solve, they encourage suppliers to innovate. Sustainable procurement can thus drive product and process innovations, opening up new market opportunities. For example, greener materials or more efficient production methods can emerge from collaborative efforts. These innovations make the supply chain more efficient and adaptable.
Social Responsibility

Beyond business value, sustainable procurement meets growing demands for social and ethical accountability. Today’s stakeholders – from communities and NGOs to customers and regulators – expect companies to consider environmental and social impacts. By doing so, organizations maintain their social license to operate and reputation. Sustainable procurement aligns a company with its stakeholders’ values, which reduces reputational risk and keeps the business in good standing.
Meeting Stakeholder Demands: Governments, NGOs, and the public increasingly pressure companies to address climate change, labor standards, and inequality. Sustainable procurement is a direct way to show commitment to these issues. It helps an organization “maintain its social license to operate” by demonstrating it listens to and acts on stakeholder values. This alignment strengthens community trust and license to operate.
Workers: Fair and sustainable sourcing often goes hand-in-hand with better labor practices. Focusing on sustainability can mean ensuring suppliers provide decent work and safe conditions. When companies prioritize their workers’ well-being and values (including among supplier workforces), employee engagement tends to rise. Research shows employees involved in sustainability initiatives feel more connected to their company’s mission, leading to higher job satisfaction and loyalty. In practice, this means higher productivity and better talent attraction and retention.
Supplier Commitment: Making sustainability a priority encourages stronger partnerships with suppliers. When suppliers see a company is committed to responsible practices, they are more likely to invest in improvements and align with those goals. Sustainable procurement thus strengthens supplier relationships, fostering collaboration and transparency. These closer ties can lead to cost savings and a more resilient supply chain overall.
Organizational Culture

Finally, sustainable procurement succeeds only when it is rooted in the organization’s culture and values. Leadership commitment and a strong ethical framework make sustainability part of everyone’s mindset. When executives and managers lead by example – setting clear sustainability goals and providing resources – it empowers teams to integrate green practices into daily procurement decisions. Embedding sustainability into core processes makes it a habit rather than an afterthought.
Leadership and Culture: Change starts at the top. When senior leaders champion sustainable procurement, they create a culture where environmental and social concerns are “baked into” every purchase decision. This might include training buyers on sustainability criteria or setting KPIs for supplier sustainability. Over time, these practices become routine habits, ensuring consistent application of sustainability without constant oversight.
Ethical Alignment: Aligning procurement with the organization’s ethics and values strengthens the company’s integrity. By prioritizing sustainability, a company demonstrates that its actions match its stated values and mission. This builds internal trust and external credibility. In short, sustainable procurement reflects a deeper commitment to doing business ethically, which bolsters the organization’s overall reputation and cohesion.
Conclusion
In summary, sustainable procurement offers holistic value that spans market success, operational strength, social impact, and internal culture. By meeting customer and stakeholder expectations, businesses gain loyalty, stand out against competitors, and attract investment. By managing environmental and social risks, they protect the brand, ensure steady supply, and spark innovation. And by embedding sustainability into their culture and ethics, they rally employees and partners around shared values. In this way, sustainable procurement becomes more than a policy – it becomes a strategic advantage that can drive economic success, mitigate risks, foster innovation, and secure the future of the company. Ultimately, these drivers show that investing in sustainable procurement is not just good for the planet and society; it’s also smart business.


I just couldn’t leave your site before suggesting that I really enjoyed the standard information an individual provide in your visitors? Is going to be again regularly to check up on new posts
Thanks for any other informative website. The place else may I get that kind of information written in such a perfect manner? I’ve a undertaking that I’m simply now operating on, and I have been on the look out for such info.
Have you ever thought about adding a little bit more than just your articles? I mean, what you say is valuable and all. Nevertheless just imagine if you added some great visuals or video clips to give your posts more, “pop”! Your content is excellent but with pics and clips, this website could undeniably be one of the very best in its niche. Excellent blog!
It’s interesting how considering environmental and social factors can actually build brand value, as the article mentions. I also found a helpful overview of related supply chain considerations on https://seed3d.ai.
LuckyKingVIP… sounds fancy, right? I was a bit skeptical at first, but they’ve actually got some cool games and a good VIP program if you’re into that sort of thing. Feeling lucky? Give it a whirl. luckykingvip
I find dudoanxsmb to be a game changer. Payouts are quick and the interface is really easy to use. Give dudoanxsmb a shot and let me know how you like it
Sodo Casino Earthgang? Nghe cái tên là thấy chất chơi rồi đó. Có ai từng thử vận may ở đây chưa? Share tí kinh nghiệm nào! Check it out yourself: sodocasinoearthgang
212betlogin, man, that login is so smooth! Get in, get bets placed, get paid! Can’t beat it. 212betlogin
Trying the fruit party demo on fruitparty.net is a smart idea. I was hooked instantly after playing it. You gotta test drive the demo first, trust me! See for yourself right here fruit party demo
You really make it seem so easy along with your presentation however I in finding this matter to be really something that I believe I’d never understand. It kind of feels too complicated and extremely extensive for me. I am taking a look forward to your subsequent post, I?¦ll attempt to get the dangle of it!
I really enjoyed playing. slice n stack has some interesting mechanics that keep you coming back for more.