When people talk about who’s to blame for climate change, they often point fingers at businesses. Nowadays, everyone’s talking about cutting down on the pollution that causes climate change. But how do companies even start with such a confusing task? How can they tell if they’re making progress?
A long time ago, in 1954, a smart guy named Peter Drucker gave us a clue: “what gets measured, gets managed.”
So, if a company really wants to be more environmentally friendly and do better for the planet, the first thing it should do is figure out how much pollution it’s creating. That means keeping an eye on how much carbon dioxide, a big contributor to climate change, it’s putting into the air.
But here’s the catch: figuring out how much carbon pollution you’re making isn’t easy. Nowadays, most big companies are doing it. Even companies like Apple, Facebook, and even the big oil companies like Shell and BP are keeping track of how much carbon pollution they’re making. And it’s not just because their bosses care about the environment.
Here’s the deal: less carbon pollution equals lower costs. When companies figure out how much carbon pollution they’re making, it helps them see if they’re wasting energy or not using it efficiently. When they cut down on carbon pollution, they often end up saving money because they’re running things more efficiently.
Now, let’s dive into understanding carbon footprint and how it is calculated,
Understanding Carbon Footprint
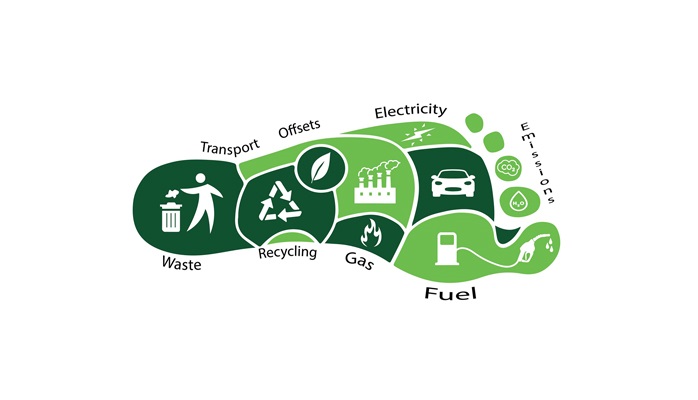
A “carbon footprint” is like a measurement of how much stuff we do or make that causes climate change. It’s about the gases we send into the air, like the ones that make the Earth warmer. These gases can trap heat in the air and make our planet get hotter. So, a carbon footprint tells us how much we’re contributing to this problem by doing certain things or making certain things.
Components of Carbon Footprint
When we talk about a “carbon footprint,” we mean all the different ways a company or organization contributes to climate change. It’s important for them to understand these ways so they can try to reduce their impact on the environment.
Here are the three main parts that make up a company’s carbon emissions:
- Scope 1 – Direct Emissions: This is about the pollution that comes directly from things the company owns or controls, like factories, cars they use, or machines they operate.
- Scope 2 – Indirect Emissions: These emissions come from the electricity or energy the company buys to run its operations. It’s like the pollution created when making the energy they use.
- Scope 3 – Other Indirect Emissions: These are emissions from things related to the company’s activities but not directly owned by them. For example, it includes the pollution from making the materials they use, transporting their products, and dealing with waste.
In addition to these scopes, there are different types of carbon footprints depending on what’s causing the pollution:
- Product Carbon Footprint: This looks at the pollution created by a product or service from the time its materials are taken from the earth to when it’s no longer used.
- Corporate Carbon Footprint: This includes all the pollution from a company’s buildings, operations, and everything it does.
- Operational Carbon Footprint: It’s the pollution that happens every day because of how the company runs its operations, like using energy, transportation, and managing waste.
Understanding these different parts of a carbon footprint helps organizations figure out where they can make changes to reduce their impact on the environment.
Calculating Carbon Credit
Once you understand how you add to the pollution that affects the planet, the next step is to figure out how much of that pollution you’re actually responsible for. One common way to do this is by using something called the “greenhouse gas protocol.”
This method works by turning different types of pollution into a standard measure, like carbon dioxide (CO2), based on how much they contribute to global warming. Once you’ve done this conversion, you can measure the actual amount of CO2 emissions in metric tons to see how much pollution your company or organization is producing.
Impact of Carbon Footprint on Business
From a purely business perspective, investing in lowering carbon emissions may seem counterproductive. However, that’s not remotely true.
On the surface level, reducing carbon emissions is expensive and offers no return. However, while you may not earn directly from it, such initiatives will enhance your company’s financial position in the long run.
Below are some of the advantages your organization will get by monitoring carbon footprint,
Benefits of Monitoring Carbon Footprint
- Environmental Responsibility: By monitoring emissions, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to environmental responsibility and sustainability. This can enhance their reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious customers, investors, and stakeholders.
- Compliance with Regulations: Many regions and countries have regulations in place that require organizations to monitor and report their emissions, especially greenhouse gases. Monitoring helps ensure compliance with these laws, which can prevent legal issues and fines.
- Cost Reduction: Monitoring emissions can identify areas of inefficiency or waste in an organization’s processes. Once these areas are identified, steps can be taken to reduce emissions, leading to cost savings in terms of energy consumption, resource usage, and waste management.
- Energy Efficiency: Monitoring emissions often involves tracking energy consumption. Organizations can use this data to implement energy-saving measures, such as upgrading equipment, optimizing processes, and reducing energy waste. This leads to lower energy bills and reduced carbon emissions.
- Risk Mitigation: By understanding their emissions profile, organizations can identify potential environmental risks. This proactive approach allows them to develop strategies to mitigate those risks, such as adapting to changing climate conditions or addressing supply chain vulnerabilities.
- Improved Sustainability Reporting: Many organizations produce sustainability reports to showcase their environmental efforts. Accurate and comprehensive emission data is crucial for creating these reports and demonstrating progress toward sustainability goals.
- Competitive Advantage: Organizations that actively monitor and reduce their emissions can gain a competitive advantage. They may attract environmentally conscious customers, win contracts with green procurement requirements, and stand out as leaders in their industry.
- Investor and Shareholder Confidence: Investors and shareholders increasingly consider environmental performance when making investment decisions. Emission monitoring and reduction efforts can boost investor confidence and attract investments from environmentally focused funds.
- Supply Chain Management: Organizations can use emission data to assess the carbon footprint of their supply chain. This information can help identify eco-friendly suppliers and promote sustainable sourcing practices.
- Innovation and Research: Emission monitoring often leads to innovative solutions and research into sustainable technologies and practices. This can foster a culture of innovation within the organization.
- Resilience: Understanding emissions and their sources allows organizations to build resilience against climate change impacts. This includes planning for extreme weather events, supply chain disruptions, and other climate-related challenges.
- Employee Engagement: Employees tend to be more engaged and satisfied when they work for organizations that prioritize sustainability. Emission monitoring and reduction initiatives can boost employee morale and attract talent.
Overall, monitoring emissions in organizations not only helps protect the environment but also offers a range of economic, regulatory, and reputational benefits that contribute to long-term success and sustainability.
Conclusion – The sustainable market is not going anywhere
Being aware of sustainability, or taking care of the environment and being responsible, is something that’s becoming more and more important. In the business world, people are buying more products that are good for the environment, as you can see in the graph about sustainable product sales in the U.S. This trend is making companies all along the supply chain want to use more eco-friendly options. When you measure and reduce the pollution your company makes, you can say with proof that your company is doing well in terms of sustainability.
It’s not just customers who care about this. Employees also really care about the environment, and they like working for companies that do too. In fact, companies that are good for the environment can attract and keep talented employees more easily.
Even investors, the people who put money into companies, are paying more attention to sustainability. They look at things like how a company treats the environment, how it treats people, and how it’s run. This means that if a new company wants investors, it’s a good idea to show that it cares about the environment. And for companies that have been around a while, keeping track of environmental information can help them understand how well they’re doing in terms of productivity, products, and the market.