Carbon credits are a key component of emissions trading systems and carbon offset projects. They are a way to incentivize and facilitate the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2) and other pollutants, that contribute to climate change. Carbon credits are a tradable commodity that represents a unit of emissions reduction or removal from the atmosphere. They are used as a mechanism to meet emission reduction targets and promote sustainability efforts by allowing entities to offset their own emissions by investing in projects that reduce emissions elsewhere.
Origin and Purpose
Carbon credits originated as a result of the need to address the challenge of climate change caused by the accumulation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. The primary greenhouse gas is carbon dioxide (CO2), but other gases like methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O) also contribute. To combat the negative effects of these gases, carbon credits were introduced as a way to create a market-based mechanism for reducing emissions.
Measurement of Emissions Reductions
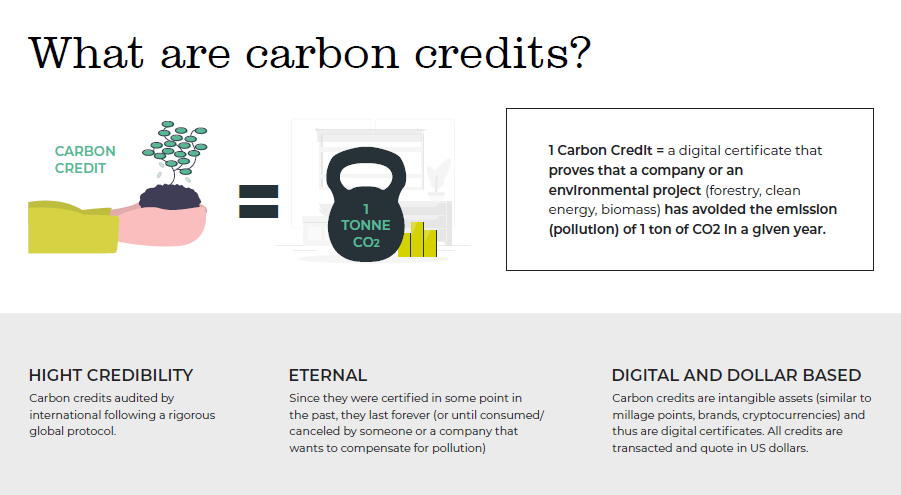
Carbon credits are typically measured in metric tons of CO2-equivalent (CO2e). This standardizes the measurement of different greenhouse gases by expressing their warming potential in terms of the equivalent amount of CO2.
Types of Carbon Credits
Carbon credits can be categorized into two main types:
- Cap-and-Trade Credits: In cap-and-trade systems, governments set a limit (cap) on the total allowable emissions within a certain jurisdiction. These allowances are then distributed or auctioned to companies or entities. If a company emits fewer emissions than its allotted allowances, it can sell the surplus allowances to companies that exceed their emissions limits.
- Offset Credits: Offset credits are generated from projects that reduce or remove emissions from the atmosphere. These projects can include reforestation, renewable energy projects, methane capture from landfills, and more. Each offset credit represents a quantifiable reduction of emissions, and they can be bought by entities seeking to compensate for their own emissions.
Emission Reduction Projects
Carbon offset projects are implemented to generate carbon credits. These projects follow established methodologies and protocols to calculate the emissions reduction achieved. For example, a reforestation project might measure the amount of CO2 sequestered by the newly planted trees, and this reduction is then translated into carbon credits.
Verification and Certification
Carbon offset projects undergo a rigorous process of verification and certification to ensure that the claimed emissions reductions are accurate and credible. Independent third-party verifiers assess the project’s methodologies, data, and outcomes to confirm that the promised reductions have been achieved.
Trading and Marketplaces
Carbon credits are traded on various carbon markets. These markets allow entities to buy and sell credits to fulfill their emission reduction obligations. The price of carbon credits can vary based on supply and demand dynamics, the stringency of emission reduction targets, and market sentiment.
Role in Climate Mitigation
Carbon credits play a crucial role in climate mitigation by providing financial incentives for emission reduction activities. They enable companies and countries to take responsibility for their emissions and invest in sustainable projects, even if they cannot achieve complete emissions reductions themselves.
International Frameworks
International agreements, such as the Kyoto Protocol and the Paris Agreement, have provided a framework for countries to set emission reduction targets and collaborate on climate action. Carbon credits can be used to help countries meet their commitments under these agreements.
Conclusion
In summary, carbon credits are a market-based approach to addressing climate change. They encourage emissions reductions by putting a price on carbon and providing a mechanism for entities to invest in emissions reduction projects. While they have been effective in driving sustainable practices, there are also debates about their effectiveness and potential for market manipulation. The concept of carbon credits continues to evolve as the world seeks more comprehensive solutions to combat climate change.