What are Carbon Standards?
A carbon standard—or GHG crediting program—refers to the complete set of rules, procedures, and methodologies according to which certified carbon credits are generated and issued.
Carbon standards are developed and governed by standard organizations—typically international non-governmental organizations (NGOs) that consists of a standard-setting arm, a regulatory arm, and a validation and verification system are usually outsourced to third parties.
Governments can also develop or support the development of carbon standards, such as the Woodland Carbon Code in the United Kingdom and the Thailand Voluntary Emission Reduction Program.
By developing and administering standardized procedures for crediting greenhouse gas (GHG) emission reductions, avoidance, and removals, standard organizations act as the regulators of the VCM.
Given the voluntary nature of this market, standard organizations safeguard the quality of VCM carbon credits and provide credibility to the baseline-and-credit system on which the VCM relies.
Carbon standards both certify carbon projects and programs and facilitate the trade of carbon credits.
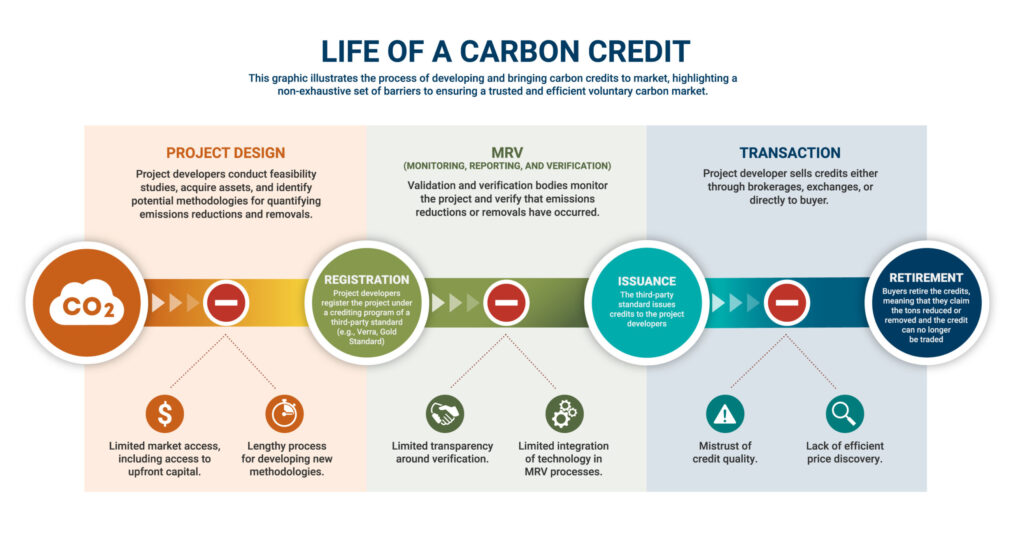
- To obtain certification of GHG emission reductions or removals and be issued credits to trade, VCM projects and programs must comply with standards.
- processes, rules, requirements, and safeguards
- apply methodologies approved by the standards
- provide evidence of compliance that is generated by the activity managers and reviewed by an independent third-party auditor.
- Carbon standards use registries to track all credits generated, transfer tradable credits, and trace transactions between buyers and sellers.
The most popular carbon standards widely used today include the Greenhouse Gas Protocol (GHG Protocol), ISO 14064, Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP), Verra (Verified Carbon Standard), and Gold Standard. The GHG Protocol, developed by the World Resources Institute (WRI) and the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD), is the globally recognized standard for carbon accounting, providing comprehensive guidelines for measuring and reporting emissions. ISO 14064, a series of international standards by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), offers guidelines for quantifying and reporting greenhouse gas emissions and removals. The CDP encourages organizations to disclose environmental data, including carbon emissions and serves as a benchmark for corporate environmental transparency. Verra and Gold Standard are reliable standards for certifying carbon offset projects, ensuring rigorous methodologies, and social and environmental co-benefits. These standards collectively promote transparency, accountability, and consistency in carbon management across various sectors, assisting organizations, governments, investors, and consumers in their efforts to address climate change.
ProducerS
In CROWN MONKEY we refer producers to those Green Organizations that generate carbon credits with their sustainable practices. In our system, we are trying to automate the process of allotment of credits to the Green Organizations and keep the approver process at last to give them better result-based visualizations and opportunities for those green organizations that follow innovative sustainable approaches.
Benefits of Crown Monkey Automated and Reliable Carbon Credit Allotment System
- Approve at Last: This will give a better result-based visualization to approvers and better opportunities for green organizations to showcase their energy-saving capabilities with their new and innovative sustainable approaches.
- Automated: IoT devices are used to gather emission data and with the help of a comparison formula, an equivalent amount of generated credit is calculated thus eliminating traditional ways of using manually predefined values.
- Transparent: All these measuring devices are integrated with the Blockchain network, therefore all data collected is tamper-proof and stored transparently thus maintaining the trust and feasibility of the system.
- Digital Certification: All the information such as measured results of green projects and their methodologies are shared with approvers and after successful approval, digital certification is generated on Blockchain that holds the validity of credits.
- Immediate allotment: After successful approval credits are allotted immediately to the wallet of green organizations that can further be used for trade.