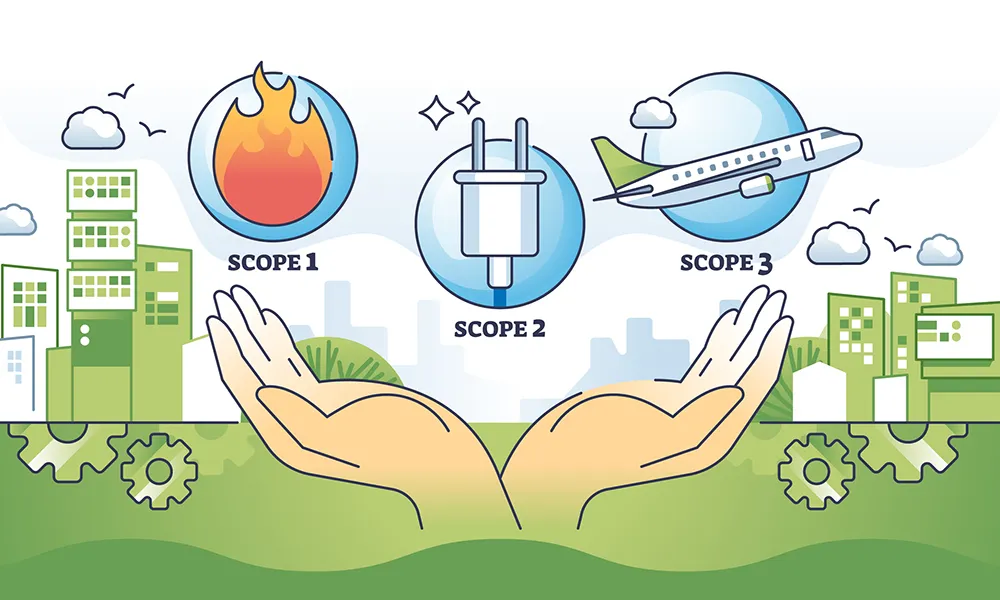
Reducing carbon footprints has become a crucial goal for businesses across industries. While Scopes 1 and 2 emissions—those generated directly by companies or indirectly from energy consumption—are often prioritized, Scope 3 emissions represent a more complex challenge. These emissions occur across the value chain, from suppliers to end-users. Addressing them not only meets growing regulatory demands but also uncovers significant business opportunities. This blog explores strategies and insights for reducing Scope 3 emissions and highlights potential value-creation pathways.
Understanding Scope 3 Emissions
Scope 3 emissions encompass all indirect emissions that occur in a company’s value chain. These emissions often account for the majority of a company’s total greenhouse gas emissions, making them a critical target for decarbonization efforts. Regulatory pressures, such as the Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR) in Europe, require businesses to report Scope 3 emissions, emphasizing the urgency of developing effective strategies.
Strategic Approaches to Scope 3 Emissions
Supplier and Customer Selection
- Dual-Mission Sourcing: Companies are now prioritizing suppliers that minimize both cost and carbon footprint. For example, Volvo Trucks is designing vehicles using fossil-free steel through partnerships with Swedish steel manufacturers. Collaboration with suppliers and customers to reduce emissions during product use can significantly lower overall emissions.
Product Specification and Solutions
- Lifecycle Design: Automotive companies, such as BHP and HBIS, are adapting product designs to reduce input emissions and enhance fuel efficiency. By integrating low-carbon materials and optimizing product specifications, businesses can achieve substantial emission reductions during the use phase.
Partnerships
- Technological Innovation: Collaborations across the value chain are essential for developing new technologies. For instance, mining company Vale and steelmaker Boston Metal partnered to create molten-oxide electrolysis technology, enabling lower-carbon steel production.
End-of-Life Solutions
- Circular Economy: Recycling and circular solutions reduce both upstream and downstream emissions. Companies like Ørsted and Salzgitter are integrating circularity in their processes by using recycled materials for production.
Green Portfolio Strategies
- New Business Segments: Transitioning to green business segments can create value and reduce carbon footprints. Schneider Electric, for example, shifted from providing hardware to focusing on energy management solutions.
Value Chain Integration
- Upstream and Downstream Integration: Controlling emissions along the value chain can lead to significant reductions. Mining company LKAB moved downstream to process iron using direct reduction methods, improving emission controls.
Industry-Specific Strategies
Different industries face unique challenges and opportunities when addressing Scope 3 emissions:
- Automotive: Focus on electrification and low-carbon supply chains.
- Chemicals: Sourcing low-carbon or bio-based feedstocks.
- Mining: Partnering with downstream players for low-emission processing technologies.
- Building Materials: Collaborating with suppliers to decarbonize production and revise product specifications.
Critical Success Factors
- Baseline Emissions: Develop a granular understanding of Scope 3 emissions to target key areas effectively.
- North Star Vision: Align emission reduction targets with value creation opportunities, ensuring customer demand for greener products is met.
- Cross-Functional Teams: Foster collaboration across business units to integrate decarbonization efforts seamlessly.
- Value Chain Partnerships: Engage in partnerships to enhance transparency and achieve shared decarbonization goals.
- Data and Tracking Standards: Collaborate on setting industry standards for emissions tracking and transparency.
- Capability Building: Establish academies to upskill the workforce in sustainability and emissions management.
- Incentives: Implement internal carbon pricing to integrate emissions into decision-making processes and incentivize reductions.
Reducing Scope 3 emissions is not just about compliance; it represents a strategic opportunity for businesses to innovate, create value, and lead in sustainability. By leveraging partnerships, optimizing product designs, and integrating across the value chain, companies can transform their business models and achieve significant strides toward net-zero emissions. The time to act is now—embrace the challenge and unlock the potential of a greener future.